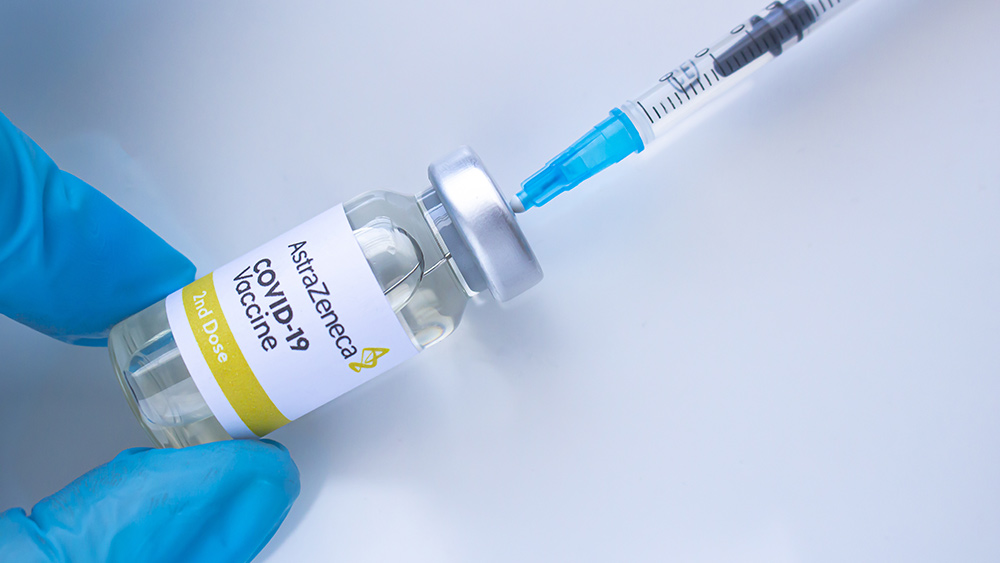
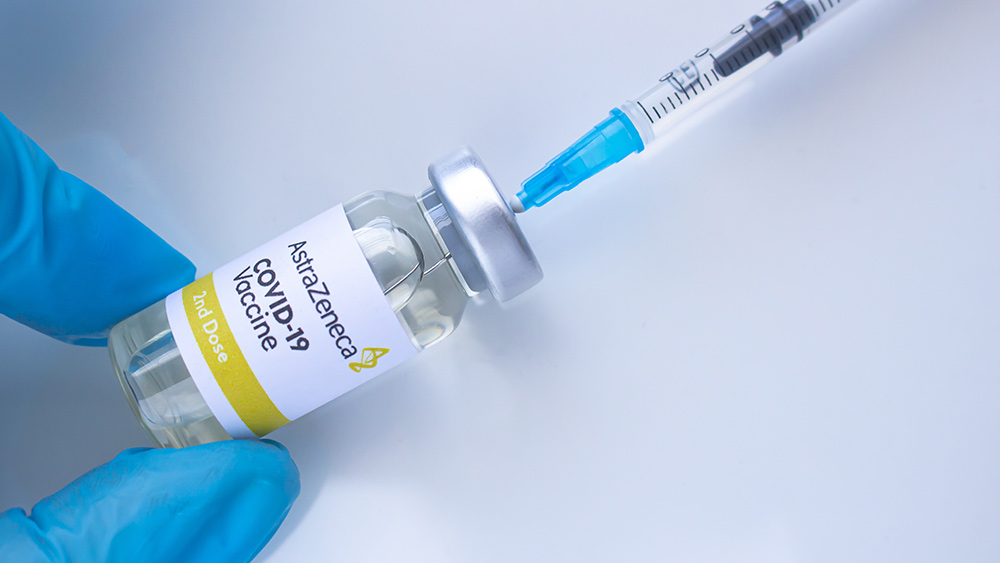
A group of Australian scientists called on the country's federal government to review its use of AstraZeneca's coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccine. They argued that the jab is ineffective at generating herd immunity and has a low efficacy rate. However, the central government has rejected the proposal to pause the rollout scheduled next month.
The opposition Labor Party and some immunologists have called on the Australian government to procure additional doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. Clinical trials for these two vaccines have shown that they have higher efficacy rates than the one produced by AstraZeneca.
"Until we get more data [showing] that AstraZeneca is as good as the others, the scientific and medical risk that you take is that you won't get herd immunity," said Australian Medical Association in Western Australia (AMA-WA) President Andrew Miller. He also warned that there could be a political risk for having a good vaccine for the rich and a not-so-good vaccine for the poor.
To avoid these risks, Miller said Australia should halt the planned rollout and source the best vaccines available to build public confidence.
However, the central government in Canberra said the AstraZeneca vaccine – developed in partnership with the University of Oxford – would provide vital protection against the Wuhan coronavirus. Australia's Chief Medical Officer Paul Kelly said that the AstraZeneca vaccine is effective, safe and high-quality, and will be available in the country once the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration approves it in February.
The British drug maker has agreed to supply Australia with 53 million vaccine doses, which, according to clinical trials, has a 70 percent efficacy rate. Australia has also ordered 10 million doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine – to be approved by the Australian regulator next month.
Some scientists have expressed concern over Canberra's reliance on inaccurate AstraZeneca vaccine data
Back in November 2020, a scientist-turned-writer pointed out the "shaky science" behind the AstraZeneca vaccine data. In a piece for Wired magazine, Hilda Bastian highlighted many issues with the so-called "promising results" released by the drug maker.
Bastian pointed out that a "dosing error," which was never explained, allowed the company to report a higher efficacy rate for their vaccine. Two standard doses of AstraZeneca's Wuhan coronavirus jab achieved a 62 percent efficacy rate. However, volunteers given an initial half-dose and a subsequent full dose reported a higher efficacy rate of 90 percent. Bastian noted that AstraZeneca's clinical trials were designed to examine the effect of the standard two-dose regimen, not the accidental dosing.
In addition, Bastian noted that AstraZeneca's data came from two separate studies. These studies – one published in May 2020 and another at the end of June 2020 – were substantially different from each other. "The fact that they may have had to combine data from [these] two trials in order to get a strong result raises … [a] red flag," she commented.
A number of Australian scientists have expressed concern about the central government's reliance on the AstraZeneca jab, including Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology (ASI) President Stephen Turner.
The ASI president said shifting to higher-efficacy vaccines "looks like a good idea in an ideal situation." He added that a review of Australia's vaccine strategy would be appropriate. However, procuring and rolling out the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also presents challenges as it needs to be stored at a temperature of -70 degrees Celsius.
Turner nevertheless remarked that the AstraZeneca jab could be a useful tool in the short term. The vaccine can be kept at temperatures between two to eight degrees Celsius, eliminating the need for specialized facilities. Aside from the lower temperatures needed for storage, AstraZeneca's vaccine also has the lowest price compared to the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna candidates.
Despite its reported advantages, the AstraZeneca vaccine hit multiple roadblocks in earlier clinical trials. Last September, two participants were reported to have experienced spinal inflammation after receiving the shot, while a third participant died during clinical trials in Brazil a month later. Further investigation revealed that toxic ingredients in the jab, such as aborted human fetal tissue, contributed to the adverse effects associated with the vaccine.
Vaccines.news has more on the AstraZeneca jab and other Wuhan coronavirus vaccine candidates.
Sources include:
Please contact us for more information.