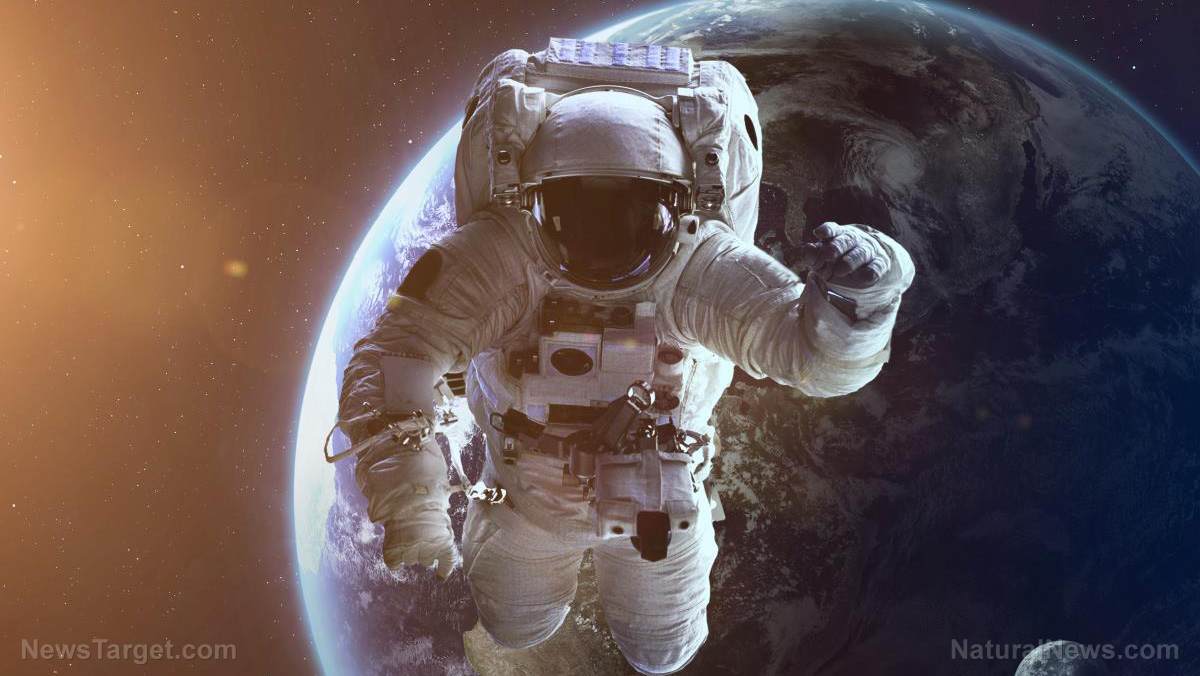
New research from NASA has found that resveratrol, one of the key medicinal ingredients in grapes and red wine, may be beneficial in helping astronauts on future long missions to Mars avoid developing serious health conditions like muscle atrophy.
Even though the scientific establishment often insists that food nutrients like resveratrol are functionally useless for people on Earth, NASA says they're great for people up in space who need extra strength to survive long treks across the universe.
Research has shown that resveratrol, the highest concentrations of which are found in the skin of grapes, helps preserve bone strength and muscle mass, as well as protect against muscle wasting. Resveratrol is also a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound, which means it's an all-around good thing for the human frame.
In anti-gravity conditions, especially, the human body can't exert itself the same way it would on Earth, meaning muscles and bones are likely to deteriorate over time. Resveratrol, however, can prevent this from happening, which is why NASA scientists are now recommending it as a new space protocol.
Tests involving mice have shown that, compared to rodents not taking the supplement, resveratrol helped to substantially strengthen their bones and enhance their muscle mass in a simulated Mars low-gravity situation.
"After just three weeks in space, the human soleus muscle shrinks by a third," says Dr. Marie Mortreux, lead author of the study. "This is accompanied by a loss of slow-twitch muscle fibers, which are needed for endurance."
Since astronauts on missions to Mars won't have the same exercise machines that are currently present on the International Space Station (ISS), "dietary strategies" that include resveratrol, contends Mortreux, may offer the next best thing.
Resveratrol shown to protect against radiation poisoning
Another benefit of resveratrol is its ability to mitigate the deleterious effects of ionizing radiation. Since astronauts traveling to Mars are exposed to up to 700 times the amount of radiation that's present here on Earth, they need extra protection while they work.
Solar flare activity and the radiation it releases in space is known to cause acute damage in the form of blood damage, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Long-term exposure can lead to cataracts, sterility, and of course cancer, as well as damage to the brain, central nervous system and heart.
Research published in the journal BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine found that resveratrol is helpful in mitigating radiation-induced small intestine injuries, as it counteracts cell apoptosis and other forms of DNA damage.
"Compared to the vehicle control, treatment with resveratrol improved intestinal morphology, decreased apoptosis of crypt cells, maintained cell regeneration, and ameliorated SOD2 expression and activity," the paper found.
"Resveratrol also regulated Sirt1 and acetylated p53 expression perturbed by irradiation in the small intestine. The protective effect of resveratrol against ionizing radiation induced small intestine injury was significantly inhibited by Ex527."
According to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, resveratrol can actually help to stop certain types of cancer cells from dividing, as well as protect against the harmful side effects of radiation treatments – all this suggesting that the nutrient could be a viable solution for astronauts in need of supplementary support while traveling through space.
"Resveratrol treatment promotes muscle growth in diabetic or unloaded animals, by increasing insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in the muscle fibers," adds Dr. Mortreux about resveratrol's other benefits.
"This is relevant for astronauts, who are known to develop reduced insulin sensitivity during spaceflight … Further studies are needed to explore the mechanisms involved, as well as the effects of different doses of resveratrol (up to 700 mg/kg/day) in both males and females."
Sources for this article include:
Please contact us for more information.