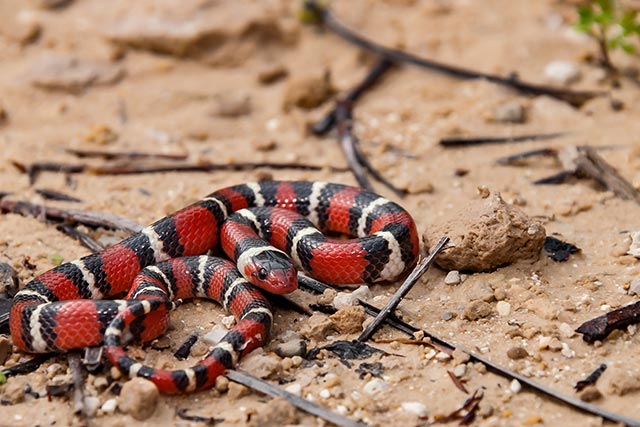
A biomedical scientist by the name of Zoltan Takacs created a biotechnology startup called ToxinTech that currently lists some 16 different pharmaceutical drugs that are made from the peptides of snake and other animal venom.
ToxinTech houses a library of 'designer toxins' that researchers can access in order to study new drug development ideas.
"We're actually not only creating toxin libraries, we're doing a twist," Takacs told CNN back in 2020 during the height of the Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) plandemic when some doctors were using venom-based drugs like Integrilin, which is made from the venom of the pygmy rattlesnake, to treat COVID blood clots.
"If we have a target for which there is not a good molecule which blocks that target, for example, then we look (to) nature. What kind of toxins around the world exists which target that particular molecule?"
Takacs went on to explain that these animal venom peptides are made using biotechnology (GMO). The end result is "mosaic toxins" that he says still contain the same "evolutionary wisdom" as the real venom found in animals.
Did you know this many drugs were made from animal venom?
The following venom-based drugs are listed on ToxinTech as being approved and currently in clinical use:
• captopril (CAPOTEN), an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor drug made from the venom of the jararaca pit viper snake (Bothrops jararaca)
• enalapril (VASOTEC), another angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor drug made from the venom of the jararaca pit viper snake (Bothrops jararaca)
• exenatide (BYETTA), a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist drug made from the venom of the Gila monster lizard (Heloderma suspectum)
• exenatide (BYDUREON), an extended release version of BYETTA also made from the venom of the Gila monster lizard (Heloderma suspectum)
• ziconotide (PRIALT), a Cav2.2 channel antagonist drug made from the venom of the magical cone marine snail (Conus magus)
• bivalirudin (ANGIOMAX), a reversible direct thrombin inhibitor drug made from the venom of the European medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis)
• lepirudin (REFLUDAN), a drug that binds irreversibly to thrombin and that is also made from the venom of the European medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis)
• desirudin (IPRIVASK), a selective and near-irreversible inhibitor of thrombin, similar to REFLUDAN, that is also made from the venom of the European medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis)
• tirofiban (AGGRASTAT), an antagonist of fibrinogen binding to the GPlIb/lIla receptor drug made from the venom of the saw-scaled viper snake (Echis carinatus)
• eptifibatide (INTEGRILIN), a drug that prevents binding of fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, and other adhesive ligands to GPIIb/IIIa, that is made from the venom of the pigmy rattlesnake (Sistrurus miliarius)
• batroxobin (DEFIBRASE), a drug that cleaves A?-chain of fibrinogen and is made from the venom of both the common lancehead snake (Bothrops atrox) and the Brazilian lancehead snake (Bothrops moojeni)
• platelet gel (PLATELTEX-ACT), a drug similar to DEFRIBRASE that is made from just the venom of the common lancehead snake (Bothrops atrox)
• fibrin sealant (VIVOSTAT), a drug similar to the previous two that is made from the venom of just the Brazilian lancehead snake (Bothrops moojeni)
• thrombin-like enzymes, a class of fibrinogenase drugs made from the venom of the Chinese moccasin snake (Deinagkistrodon acutus), the Siberian pit viper snake (Gloydius halys), or the Ussuri mamushi viper (Gloydius ussuriensis)
• hemocoagulase, a drug that cleaves A?-chain of fibrinogen; factor X and/or prothrombin activation, and is made from the venom of the common lancehead snake (Bothrops atrox), jararaca pit viper snake (Bothrops jararaca), or the Brazilian lancehead snake (Bothrops moojeni)
• medicinal leech therapy, which as its name suggests is made from the venom of the European medicinal leech (Hirudo verbena) or other species
More related news can be found at BigPharma.fetch.news.
Sources include:
Please contact us for more information.