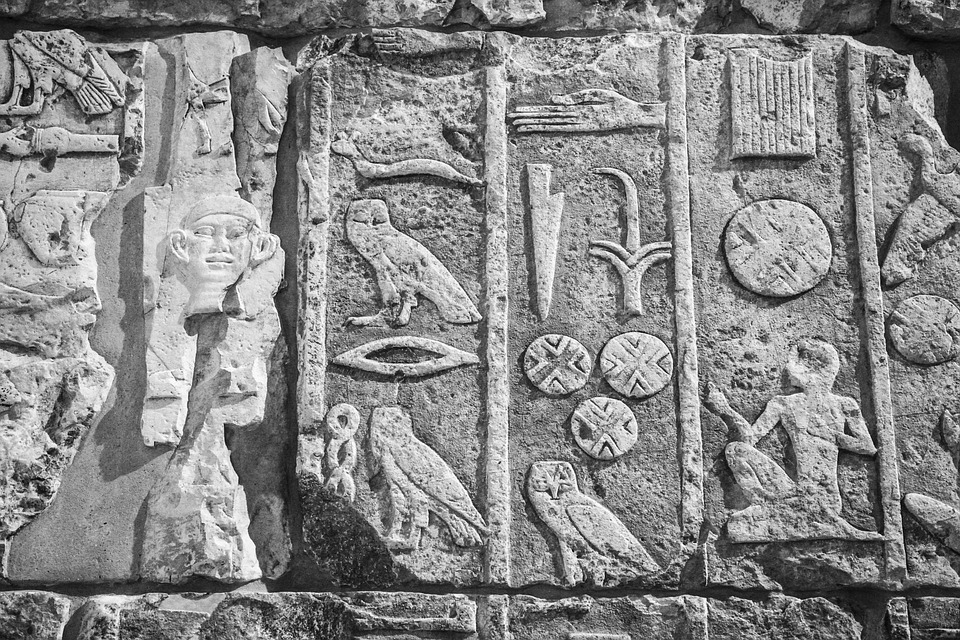
The ancient amethyst mine at Wadi el-Hudi, Egypt revealed something even more valuable than the purple-colored precious stones once extracted from there: Researchers have found more than 100 inscriptions cut into the rock of the site.
Other discoveries included 14 steles and 45 ostraca. A stele (also called stela) is an engraving on a slab or pillar of stone, while an ostracon has an engraving on a piece of pottery.
The Wadi el-Hudi Expedition researchers found that many of the inscriptions were 3,900 years old. Back then, Egypt was in its Middle Kingdom phase, roughly the equivalent of Classical Greece.
Meanwhile, they dated the majority of the ostraca to roughly 2,000 years in the past. At that point, Egypt had become part of the Roman Empire.
Amethyst is a purple-colored variety of quartz. It became very fashionable during the Middle Kingdom.
The rulers of Egypt soon discovered that Wadi el-Hudi contained large deposits of the precious stone. Expedition director Kate Lizska said that the amethyst from the mines were turned into jewelry for the ruling class.
Previous research expeditions to Wadi el-Hudi skimped on the excavation part of archeology. As a result, the early surveys failed to find many inscriptions.
“The site is just so full of inscriptions behind every boulder and around every wall that they missed a lot of them,” explained Liszka. (Related: Study concludes that the giant-leaved fig reduces oxidative stress in the liver.)
Were the workers at an ancient Egyptian amethyst mine slaves or freemen?
Liszka's team left little to chance. They used 3D modeling, reflectance transformation imaging (RTI) and photogrammetry.
Their techniques uncovered new ancient artifacts and produced accurate maps of the archeological ruins. They also took a closer look at previously discovered inscriptions.
The Wadi el-Hudi Expedition is currently racing against the clock. Ongoing operations at nearby gold mines have caused irreparable damage to the old amethyst mine site.
The researchers hope that the new inscriptions and discoveries they found at Wadi el-Hudi would tell them more about the mysterious site.
One such unresolved mystery involves the amethyst miners. No one knows for sure if the workers were slaves or freemen.
“I don't know if I'm excavating a legitimate settlement where people were treated well or if I'm excavating a prison camp,” Liszka commented.
The new evidence suggested that the miners might be freemen. Several inscriptions attributed to the workers showed that they took pride in their work.
Furthermore, Liszka and her team have not yet come across any human remains despite the dangers of mining operations. The absence of bodies suggested that the miners were freemen.
Ancient Egyptians always brought the bodies of their dead back to the Nile Valley for burial. Only slaves got left out in the desert to rot and be found by future archeologists.
Researchers wonder how Ancient Egypt supplied enough drinking water to the Wadi el-Hudi mine
Oddly, other inscriptions depicted areas where soldiers kept watch over Wadi el-Hudi. One example showed a couple of guards wrestling with each other as a way to kill time during their boring task.
The soldiers might have been stationed at the amethyst mine to protect it against external attacks. And if the miners were slaves, the guards were there to prevent any escape.
Furthermore, the researchers wondered how the miners and guards at Wadi el-Hudi got supplied with drinking water. The nearest groundwater well is 1.9 miles (3 km) away. It might also not have been around during the time of the Middle Kingdom.
The second nearest source of water is the Nile River, which happens to be 18.6 miles (30 km) away. The mine required an estimated 1,000 to 1,500 personnel. Any logistics operation would need to haul enough water for those people over a considerable distance.
Read more news about historical artifacts at Artifacts.news.
Sources include:
Please contact us for more information.